
To control anxiety, practice deep breathing, mindfulness, exercise regularly, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and seek support.
What is anxiety?

Anxiety is a feeling of worry, fear, or unease, often affecting daily activities and mental well-being.
Anxiety is a natural and adaptive human response to stress or perceived threats.
It’s a feeling of uneasiness, apprehension, or fear in anticipation of a future event or situation.
While some level of anxiety is normal and can even be beneficial in certain situations, such as helping you prepare for a challenging task or staying alert in dangerous situations, excessive or chronic anxiety can become a mental health disorder.
Here are some key points about anxiety:
Types of Anxiety Disorders:
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent anxiety.
Common anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, and others.
Symptoms:


Anxiety can manifest with a wide range of symptoms, including restlessness, irritability, muscle tension, racing thoughts, excessive worry, fear of impending doom, rapid heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, and more.
The specific symptoms can vary depending on the type of anxiety disorder.
Causes of anxiety:
Anxiety can have various causes, including genetic factors, brain chemistry, personality traits, and life experiences.
Traumatic events, chronic stress, or a family history of anxiety can increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder.
Treatment:
Anxiety disorders are treatable, and there are several effective treatment options available.
These may include psychotherapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy), medication (such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications), lifestyle changes, and relaxation techniques.
Normal vs. Disordered Anxiety:
It’s important to distinguish between normal, situational anxiety and anxiety disorders.
Normal anxiety is a temporary response to stress, while anxiety disorders involve persistent and excessive anxiety that can interfere with daily life and functioning.
Coping Strategies:
Individuals experiencing anxiety can benefit from various coping strategies, such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness and meditation, regular physical activity, and seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals.
Seeking Help:
If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety that is significantly impacting daily life, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare provider or mental health professional.
They can assess the situation, provide a diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Anxiety is a common mental health issue, and with the right treatment and support, many people can manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
What are the causes of anxiety?
Anxiety disorders can have multiple causes, and they often result from a combination of factors, including genetics, brain chemistry, personality, and life experiences.
Here are some common causes and contributing factors to anxiety:
Genetics:
Research suggests that anxiety disorders can run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition.
If you have a close relative with an anxiety disorder, you may be at a higher risk.
Brain Chemistry:
Neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain, play a role in regulating mood and anxiety.
An imbalance in these neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, can contribute to anxiety.
Trauma or Stressful Life Events:
Experiencing traumatic events, such as abuse, accidents, natural disasters, or significant life changes like divorce or the death of a loved one, can trigger anxiety disorders.
Chronic stress can also lead to anxiety over time.
Personality Factors:
Certain personality traits and characteristics can make individuals more susceptible to anxiety.
For example, perfectionism, low self-esteem, and a tendency to be overly self-critical may contribute to anxiety disorders.
Environmental Factors:
Growing up in a chaotic or unstable environment, exposure to violence or constant stress, and a lack of supportive relationships can increase the risk of anxiety disorders.
Medical Conditions:
Some medical conditions, such as heart disease, thyroid disorders, and chronic pain, can lead to symptoms of anxiety.
Substance abuse or withdrawal from drugs and alcohol can also trigger anxiety.
Brain Abnormalities:
Abnormalities in brain structure or function, such as an overactive amygdala (the brain’s fear center) or imbalances in the HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis, can contribute to anxiety disorders.
Medications or Substance Use:
Certain medications, including some stimulants, steroids, and even caffeine, can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
Additionally, substance abuse or withdrawal from drugs and alcohol can lead to anxiety.
Chronic Illness or Pain:
Living with a chronic medical condition or experiencing chronic pain can lead to feelings of anxiety and distress.
Personality Disorders:
Certain personality disorders, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), are associated with heightened anxiety as a core feature.
It’s important to note that anxiety disorders are complex and can vary greatly from person to person.
What triggers anxiety in one individual may not have the same effect on another.
Additionally, a combination of these factors often contributes to the development of anxiety disorders.
If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, seeking help from a mental health professional can provide guidance and support in managing and treating the condition.
What are the remedies to control anxiety?
Anxiety can be a challenging condition to manage, but some various remedies and strategies can help alleviate its symptoms.
It’s important to note that what works for one person may not work for another, and it’s often helpful to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Here are some common remedies and strategies to control anxiety:
Therapy:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety.
Exposure Therapy:
This involves gradually facing feared situations or objects to control anxiety responses.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT):
ACT focuses on accepting anxious thoughts and feelings and committing to values-based actions.
Medication:
Antidepressants:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed to control anxiety disorders.
Anti-anxiety medications: Medications like benzodiazepines can provide short-term relief for severe anxiety, but they are typically prescribed cautiously due to the risk of dependency.
Lifestyle changes:
Regular exercise: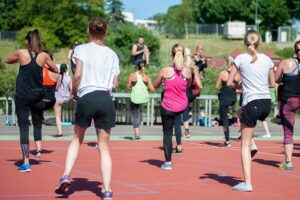
Physical activity can help reduce and control anxiety by promoting the release of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
Healthy diet:
A balanced diet can support overall well-being, and some foods may have calming effects, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids and magnesium.
Adequate sleep:
Lack of sleep can exacerbate anxiety, so establishing good sleep hygiene is important to control anxiety.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol:
These substances can trigger or worsen anxiety symptoms in some people.
Relaxation techniques:
Deep breathing exercises:
Practicing deep and slow breathing can control anxiety and help to calm the nervous system.
Progressive muscle relaxation:
This technique involves systematically tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups to reduce physical tension.
Mindfulness and meditation:
Mindfulness practices can help individuals stay present and reduce worry.
Stress management:
Time management:
Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can reduce the stress that contributes to anxiety.
Stress reduction techniques:
Activities like yoga, tai chi, and journaling can help manage stress levels.
Social support:
Talking to friends and family members about your anxiety can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation.
Support groups:
Joining a support group for individuals with anxiety can be a valuable source of understanding and coping strategies.
Self-help resources:
Self-help books and apps:
There are many resources available that offer guidance on managing anxiety and stress.
Online therapy platforms: Some people find online therapy or counseling services helpful for managing anxiety.
It’s important to remember that managing anxiety often requires a combination of these remedies and a trial-and-error approach to find what works best for you.
Additionally, if your anxiety is significantly impacting your daily life, it’s crucial to seek professional help from a mental health provider who can assess your condition and provide appropriate treatment options.
What are the home remedies to control anxiety?
Home remedies for anxiety can be helpful in managing mild to moderate symptoms, but it’s important to note that severe anxiety disorders often require professional treatment.
If you or someone you know is struggling with severe anxiety, it’s crucial to seek help from a mental health professional.
That said, here are some home remedies and self-help strategies that may help alleviate anxiety symptoms:
1. Deep Breathing:

Practice deep breathing exercises to calm your nervous system.
One effective technique is the 4-7-8 breathing method:
Inhale for a count of 4, hold for a count of 7, and exhale for a count of 8.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation:
Tense and then relax each muscle group in your body to release physical tension.
This can help reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety.
3. Mindfulness and Meditation:
Mindfulness and meditation techniques can help you stay grounded and in the present moment.
Guided meditation apps or videos can be helpful.
4. Exercise:
Regular physical activity can reduce anxiety by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
5. Diet:
Eat a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Avoid excessive caffeine, sugar, and alcohol, which can exacerbate anxiety.
Limit Stimulants:
Reduce or eliminate the consumption of stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, as they can increase feelings of anxiety.
Herbal Supplements:

Some herbal remedies, such as lavender, are believed to have a calming effect on anxiety.
Herbal Supplements:

Chamomile is reputed for its calming effects, making it a popular choice among herbal remedies.
Herbal Supplements:

The calming effects of valerian root, a popular herbal remedy, are widely acknowledged.
Consult with a healthcare professional before using herbal supplements, especially if you’re taking medications.
Aromatherapy:
Certain essential oils like lavender, rose, and chamomile can be soothing when used in a diffuser or diluted and applied topically.
Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep, as sleep deprivation can worsen anxiety.
Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
Limit Screen Time: Reduce exposure to distressing news and social media, which can contribute to anxiety.
Try to limit screen time before bedtime to improve sleep quality.
Journaling:
Write down your thoughts and feelings in a journal to help process and release emotions.
Social Support:
Talk to friends or family members about your anxiety, or consider joining a support group to connect with others who understand your struggles.
Time Management:
Organize your daily tasks and prioritize them to reduce stress and feelings of being overwhelmed.
Breathing Exercises:
In addition to deep breathing, try other breathing exercises like diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing to calm your nervous system.
Visualization:
Imagine yourself in a calm and peaceful place when you’re feeling anxious.
Visualization can help you relax and reduce stress.
Remember that what works for one person may not work for another, so it’s essential to find the home remedies and self-help strategies that resonate with you.
If your anxiety persists or worsens, consult a healthcare professional or therapist for guidance and potential treatment options.
How can I improve my anxiety naturally?
Improving anxiety naturally involves making lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits that can help manage and reduce anxiety symptoms over time.
Here are some steps you can take:
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to naturally reduce anxiety.
Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Dietary Changes:
Pay attention to your diet. Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Avoid excessive caffeine, sugar, and alcohol, which can exacerbate anxiety. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseed, and walnuts may also have a positive effect on mood.
Adequate Sleep:
Prioritize getting enough quality sleep.
Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve sleep quality.
Sleep deprivation can worsen anxiety symptoms.
Stress Management:
Learn stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, mindfulness meditation, or yoga. These practices can help you stay grounded and manage stress.
Limit Stimulants:
Reduce or eliminate the consumption of stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, as they can increase feelings of anxiety and exacerbate symptoms.
Herbal Remedies:
Some herbal supplements, such as lavender, chamomile, and valerian root, are believed to have calming effects.
Consult with a healthcare professional before using herbal supplements, especially if you’re taking medications.
Aromatherapy:
Consider using essential oils like lavender, rose, or chamomile in a diffuser or diluted in a carrier oil for topical application.
These scents are thought to have calming properties.
Cognitive-Behavioral Techniques:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques can be learned and practiced on your own or with the help of a therapist.
They can help you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety.
Social Support:
Talk to friends or family members about your anxiety, or consider joining a support group to connect with others who understand your struggles.
Social support can provide emotional relief.
Time Management:
Organize your daily tasks and prioritize them to reduce stress and feelings of being overwhelmed.
Effective time management can help you regain a sense of control.
Limit Exposure to Stressors:
Whenever possible, reduce exposure to sources of stress and anxiety in your life.
This may involve setting boundaries, saying no when necessary, or making changes in your environment.
Mindfulness and Relaxation:
Practice mindfulness techniques and relaxation exercises to stay in the present moment and reduce the physical and mental tension associated with anxiety.
Journaling:
Keeping a journal can help you process and understand your thoughts and feelings, which can be beneficial in managing anxiety.
Set Realistic Goals:
Avoid setting overly high expectations for yourself.
Set realistic and achievable goals to prevent unnecessary stress.
Professional Help:
Consider seeking help from a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, who can provide guidance, support, and evidence-based strategies to manage anxiety effectively.
Improving anxiety naturally may take time and effort, and it’s essential to be patient with yourself.
It’s also important to remember that what works for one person may not work for another, so be open to trying different strategies until you find the ones that are most effective for you.
If your anxiety is severe or significantly impacting your daily life, don’t hesitate to seek professional help for a more comprehensive treatment plan.







