
Freckles are small, brown or tan spots that can show up on the skin, especially in people with light skin. They happen when the skin makes more melanin, the substance that gives skin its color. Freckles usually appear more when the skin is in the sun, because sunlight makes the skin produce more melanin. In this article, we will look at how freckles form and what they are.

What are freckles?
These spots are small, flat, and pigmented spots that appear on the skin, typically as a result of sun exposure.
They are composed of clusters of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes.
They are most commonly found in areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, arms, shoulders, and upper back.
Important things to know about freckles:
Appearance:
Typically, they appear in shades of tan, light brown, or a reddish-brown color.
Frequently, their shape can be round or oval with clear edges.
Some people have just a few freckles, while others might have many scattered across their skin.
Causes:
They are primarily caused by an increase in melanin production in response to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
They tend to darken when exposed to sunlight and may fade during the winter months or when sun exposure decreases.
Genetic Factors:
The tendency to develop brown spots can be influenced by genetics.
People with fair skin and a family history of these spots are more likely to have them.
Types of Freckles:
Ephelides:
These are the most common types and are typically small, light brown spots that appear in childhood and darken with sun exposure.
Lentigines:
Also known as liver spots or sun spots, these are larger, darker, and more long-lasting than ephelides.
They tend to develop later in life and are more common in older individuals.
Sun Protection:
They are a sign of sun damage, and individuals with freckles are more susceptible to the harmful effects of UV radiation, including an increased risk of skin cancer.
It’s important for individuals with these spots to take measures to protect their skin from the sun, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade.
Treatment:
Many people choose to embrace their freckles as a natural feature of their skin. However, if these spots are a cosmetic concern, various treatments such as topical bleaching agents, laser therapy, or chemical peels may help reduce their appearance.
These treatments should be discussed with a dermatologist.
Difference from Moles:
They should not be confused with moles (nevi), which are typically raised and may have a different appearance.
Moles can also vary in color and size, and some may be associated with an increased risk of skin cancer.
Regular Skin Checks:
It’s important to monitor your skin for any changes in the appearance, size, shape, or color of freckles or moles. If you notice any concerning changes, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for a thorough skin examination.
While freckles are generally harmless and benign, they serve as a reminder of the importance of sun protection and skin care to minimize the risk of sun damage and skin cancer.
What are the causes of freckles?
They are primarily caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds.
The melanin-producing cells in the skin, called melanocytes, respond to UV radiation by increasing melanin production, resulting in the formation of freckles.
Here are the key causes and factors that contribute to the development of freckles:
Genetics:
Genetics plays a significant role in determining whether a person is prone to developing freckles.
Individuals with fair or light skin are more likely to have these spots, and the tendency to develop freckles can be inherited.
If parents or grandparents have these spots, their descendants may also be predisposed to them.
Sun Exposure:
Sunlight is the primary cause of freckles. When the skin is exposed to the sun’s UV rays, melanocytes respond by producing more melanin to protect the skin from further damage.
This increase in melanin production leads to the development or darkening of freckles.
Skin Type:
Individuals with fair or light skin are more susceptible to developing freckles because they have less melanin overall.
People with darker skin tones have more melanin, which provides some natural protection against UV radiation.
Age:
They tend to appear in childhood, and their development is often associated with sun exposure during early years.
They may become more pronounced during adolescence and early adulthood.
However, freckles can continue to develop and darken with additional sun exposure over time.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or with the use of certain medications or contraceptives, can influence the development of freckles.
Some individuals may notice an increase in freckles during these times, often referred to as “pregnancy mask” or “melasma.”
Artificial UV Exposure:
Exposure to artificial sources of UV radiation, like tanning beds and sunlamps, can also lead to the development of freckles.
These sources emit UV rays that stimulate melanin production in the skin.
It’s important to note that freckles are generally harmless and benign, but they serve as a visible sign of sun damage.
While some people embrace their freckles as a natural feature, others may choose to take steps to protect their skin from further UV exposure to minimize the development of new freckles or to reduce the appearance of existing ones.
Protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing (e.g., wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts), seeking shade, and avoiding excessive sun exposure can help prevent the formation and darkening of freckles and reduce the risk of skin damage and skin cancer.
What are the symptoms of freckles?
They themselves are not typically associated with symptoms, as they are benign pigmented spots on the skin.
However, some characteristics and features of freckles can be noted:
Appearance:
These spots are small, flat, and have well-defined pigmented spots on the skin.
They are usually tan, light brown, or reddish-brown in color. They often have a round or oval shape, and their appearance can vary from person to person.
Size:
They are usually small, ranging from a few millimeters to a centimeter in diameter.
They are generally smaller than moles (nevi), which can sometimes be raised and have a different appearance.
Fr are usually less substantial than moles (nevi), which can occasionally be elevated and exhibit a distinct look.
Location:

They are most commonly found on areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, arms, shoulders, and upper back.
They may also appear on other sun-exposed areas like the chest and neck.
Darkening with Sun Exposure: Freckles tend to darken when exposed to sunlight or UV radiation. This darkening can be more pronounced during the summer months or after sun exposure.
Variation in Number:
The number of freckles can vary from person to person. Some individuals may have only a few spots, while others may have numerous ones, covering a larger area of the skin.
Change Over Time:
They may become more pronounced or darken with increased sun exposure.
However, they do not typically change in size, shape, or color unless subjected to unusual stress or damage.
It’s important to note that freckles are considered harmless and are not typically associated with pain, itching, bleeding, or other discomfort.
They are a natural variation in skin pigmentation and are not a cause for medical concern.
While freckles themselves do not pose a health risk, they are often seen as a sign of sun damage.
Prolonged and excessive sun exposure can increase the risk of skin damage, premature aging, and skin cancer.
Therefore, individuals with freckles should take precautions to protect their skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade, to reduce the risk of further sun damage.
Additionally, it’s a good practice to regularly monitor your skin for any changes in freckles or the appearance of new or irregular pigmented lesions, as these changes may warrant evaluation by a dermatologist to rule out skin cancer.
What are the remedies for freckles?
They are small, pigmented spots on the skin that are often caused by exposure to sunlight.
Wrinkles are not harmful, but some people want to make them less noticeable to look better.
Even though wrinkles are safe, some people want to reduce how they look for beauty reasons.
Here are some treatments and precautions for wrinkles:
Sunscreen:

The most important step in preventing and reducing freckles is to protect your skin from the sun.
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 every day, even on cloudy days.
Reapply it every two hours when outdoors and after swimming or sweating.
Protective clothing:
Wear protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, and sunglasses, to shield your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays.
Sun avoidance:
Try to avoid direct sun exposure during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Sunless tanners:
Sunless tanning products, like self-tanning lotions or sprays, can help give your skin a tan appearance without the need for sun exposure.
These products do not increase freckling and can provide a temporary solution for those who want to mask their freckles.
Skin-lightening creams:

Over-the-counter or prescription skin-lightening creams that contain ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, or glycolic acid may help lighten freckles over time.
These products should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist to avoid potential side effects.
Chemical peels:

Dermatologists can perform chemical peels that use acids to exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of freckles.
Multiple sessions may be required for significant results.
Laser therapy:

Various laser treatments, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) and fractional laser therapy, can target and break down the melanin in freckles, leading to their gradual lightening or disappearance.
Laser therapy should be performed by a qualified dermatologist.
Cryotherapy:

In some cases, a dermatologist may use cryotherapy, which involves freezing the freckles with liquid nitrogen to remove them.
This is typically reserved for larger or more stubborn freckles.
Microdermabrasion:
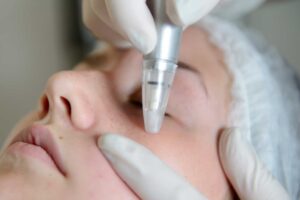
Microdermabrasion process.
This procedure involves the removal of the top layer of skin using tiny abrasive particles to improve the appearance of freckles and other skin irregularities.
Camouflage makeup:

For a quick and temporary solution, you can use makeup to cover up freckles.
Look for makeup products specifically designed for concealing blemishes and discolorations.
It’s important to consult with a dermatologist before trying any of these remedies, especially if you have concerns about your skin or if you’re considering more invasive treatments.
They can assess your skin type, and the severity of your freckles, and recommend the most suitable approach for your specific needs.
Additionally, maintaining a consistent sun protection routine is crucial to prevent the formation of new freckles and protect your skin from sun damage.
What are the home remedies for freckles?
Home remedies for freckles may not provide dramatic results like professional treatments, but they can help lighten these spots over time and contribute to overall skin health.
Keep in mind that it’s essential to be patient and consistent when using home remedies.
Here are some home remedies you can try:
Lemon juice:

Lemon juice contains natural bleaching properties due to its high acidity.
Apply fresh lemon juice to your freckles with a cotton ball and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it off with lukewarm water.
Repeat this process daily for several weeks.
Be cautious if you have sensitive skin, as lemon juice can be irritating.
Buttermilk:
Buttermilk is mildly acidic and can help lighten freckles. Apply buttermilk to your brown spots using a cotton ball and leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off. Repeat this daily.
Honey and yogurt mask:
Mix equal parts honey and plain yogurt to create a paste. Apply this mixture to your freckles and leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off.
Honey has natural skin-lightening properties, and yogurt can help soothe the skin.
Aloe vera gel:
Aloe vera has soothing and healing properties and may help reduce the appearance of freckles over time.
Apply fresh aloe vera gel to your freckles and leave it on for 20-30 minutes before rinsing it off. Repeat this process daily.
Papaya:
Papaya contains an enzyme called papain, which can help exfoliate the skin and lighten freckles.
Mash a small piece of ripe papaya and apply it to your freckles for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off. Repeat this a few times a week.
Cucumber:
Cucumber has a cooling effect on the skin and may help fade freckles. Slice a cucumber and rub the slices gently on your these spots for a few minutes.
Alternatively, blend cucumber to make a paste and apply it to your freckles for 15-20 minutes before rinsing.
Almond oil:
Almond oil is rich in vitamins and can help nourish the skin while potentially reducing the appearance of freckles.
Apply a few drops of almond oil to your freckles and gently massage it into the skin.
Leave it on overnight and rinse in the morning. Repeat this daily.
Castor oil:
Castor oil is believed to have skin-lightening properties.
Apply a small amount of castor oil to your freckles and gently massage it into the skin. Leave it on for a few hours or overnight before rinsing it off. Repeat daily.
Onion juice:
Onion juice contains sulfur compounds that may help lighten freckles. Blend or grate an onion to extract its juice and apply it to your freckles.
Leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing.
Be cautious, as onion juice may have a strong smell and can be irritating to some individuals.
Remember that results from home remedies may vary from person to person, and it can take several weeks or even months of consistent use to see any improvement.
If you have concerns about your freckles or are looking for faster results, it’s best to consult a dermatologist who can provide professional guidance and treatments.
Additionally, always use sunscreen to prevent the formation of new freckles and protect your skin from further sun damage.







