What is Uric Acid?
What is uric acid, its causes, and its treatments, are discussed in this article.
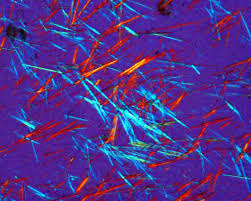
Uric acid is a chemical compound that is naturally produced in the body due to the breakdown of purines, which are substances found in certain foods and also produced by the body.
Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted through the kidneys in urine. In short, it plays a role in maintaining the chemical balance in the body.
Most of the uric acid produced in the body is dissolved in the blood and then filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine.
However, if uric acid is overproduction or the kidneys cannot excrete it efficiently, uric acid levels in the blood can become elevated.
When uric acid levels become too high, it can lead to a medical condition known as hyperuricemia.
Hyperuricemia.
Hyperuricemia is associated with various health problems, the most well-known of which is gout.
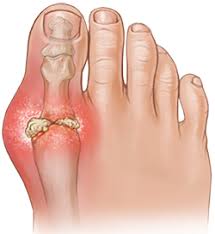
Uric acid is a chemical compound that is naturally produced in the body due to the breakdown of purines, which are substances found in certain foods and also produced by the body.
Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted through the kidneys in urine. In fact, it plays a role in maintaining the chemical balance in the body.
Most of the uric acid produced in the body is dissolved in the blood and then filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine.
However, if uric acid is overproduction or the kidneys cannot excrete it efficiently, uric acid levels in the blood can become elevated.
When uric acid levels become too high, it can lead to a medical condition known as hyperuricemia.
Hyperuricemia.
Hyperuricemia is associated with various health problems, the most well-known of which is gout.
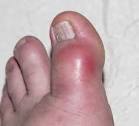
Common symptoms of gout include:
Sudden and severe joint pain, often affecting the big toe (known as podagra).
Joint redness, swelling, and warmth.
Limited range of motion in the affected joint.
Tenderness at the affected site.
Gout attacks can come on suddenly and usually peak within 24 hours.
Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis):
High uric acid levels can contribute to the formation of uric acid kidney stones.
Symptoms of kidney stones may include:
Severe lower back or side pain that can radiate to the lower abdomen and groin.
Painful urination.
Hematuria (blood in the urine).
Frequent urge to urinate.
Nausea and vomiting.
Tophi:
Tophi are urate crystal deposits that can form beneath the skin in areas such as the fingers, toes, elbows, and ears. They often appear as small, chalky nodules under the skin. Tophi can sometimes ooze a white, chalky substance.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):
Prolonged hyperuricemia can contribute to the development or worsening of chronic kidney disease. Symptoms of CKD may include fatigue, swelling (edema), changes in urine output, and elevated blood pressure.
Joint Damage:
Chronic exposure to high uric acid levels, even without gout attacks, can contribute to joint damage and the development of osteoarthritis or joint deformities over time.
Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia:
Some individuals may have high uric acid levels without experiencing any noticeable symptoms or complications. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia is often discovered during routine blood tests.
It’s important to note that not everyone with elevated uric acid levels will develop gout, kidney stones, or other related conditions.
The risk of experiencing symptoms or complications depends on various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and overall health.
If you have concerns about your uric acid levels or experience symptoms related to hyperuricemia, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and management.
In fact, early intervention and lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of gout attacks and other related health problems.
Causes of Uric Acid and its treatments.
Uric acid is produced in the body as a natural byproduct of the breakdown of purines, which are substances found in certain foods and are also produced by the body.
While uric acid production is a normal metabolic process, there are several factors that can contribute to elevated uric acid levels in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia.
Here are some common causes of and contributing factors of high uric acid levels: Its treatments are discussed in the coming paragraphs.
Dietary Factors:
Consuming a diet rich in purine-containing foods can lead to increased uric acid production. Foods high in purines include red meat, organ meats (such as liver and
kidney), seafood (especially shellfish), and certain types of beans.
Excessive alcohol consumption, particularly beer and liquor, can raise uric acid levels.
Genetics:
Genetics can play a role in determining how efficiently the body processes and eliminates uric acid. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to elevated uric acid levels.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can contribute to hyperuricemia, including:
Gout:
Gout is a condition characterized by recurrent episodes of joint inflammation due to the deposition of uric acid crystals. In fact, it is one of the most well-known consequences of high uric acid levels.
Kidney Disease:
Impaired kidney function can result in reduced excretion of uric acid, leading to its accumulation in the bloodstream.
Leukemia and Lymphoma:
Certain blood cancers can increase the breakdown of cells, leading to elevated uric acid levels.
Psoriasis:
This skin condition is associated with an increased production of skin cells, which can lead to higher levels of uric acid as these cells break down.
Hypothyroidism:
Underactive thyroid function can slow down metabolism and reduce the excretion of uric acid.
Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions such as obesity, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance are associated with elevated uric acid levels.
Medications:
Some medications can interfere with the body’s ability to excrete uric acid or increase its production. Examples include diuretics (water pills), aspirin, and certain cancer medications.
Dehydration:
Dehydration can lead to reduced kidney function, which can impair the excretion of uric acid, resulting in higher levels in the blood.
Rapid Weight Loss:
Crash diets or rapid weight loss programs that involve substantial fat breakdown can lead to elevated uric acid levels.
Injury or Surgery:
Trauma, surgery, or severe illness can lead to increased cell breakdown and subsequent elevation of uric acid levels.
It’s important to note that not everyone with high uric acid levels will develop gout or other related conditions.
Elevated uric acid levels alone may not necessarily require treatment. However, if you have concerns about your uric acid levels or if you experience symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, or kidney stones, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Depending on the underlying cause and severity, treatment options may include dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and medications to lower uric acid levels and prevent associated health issues.
Natural remedies to reduce Uric Acid.
Lowering uric acid levels naturally can be achieved through dietary and lifestyle changes.
However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant modifications to your diet or lifestyle, especially if you have gout or other related medical conditions.
Here are some natural remedies to help reduce uric acid levels:
Hydration:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help dilute uric acid in the blood and promote its excretion through the kidneys. Aim for at least 8-10 cups of water daily.
Dietary Changes:
Limit Purine-Rich Foods: Reduce or avoid foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain legumes (like lentils and dried peas).
Moderate Protein Intake:
Consume moderate amounts of lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, and tofu, instead of high-purine meats.
Increase Fiber:
Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, may help lower uric acid levels by enhancing its excretion.
Cherries:
Some studies suggest that cherries and cherry juice may help reduce gout attacks and lower uric acid levels due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
Low-Fat Dairy:
Low-fat dairy products, such as yogurt and milk, may help lower uric acid levels.
Vitamin C:
Foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, may help reduce uric acid levels.
Vitamin C supplements can also be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Coffee:
Some studies suggest that moderate coffee consumption may be associated with lower uric acid levels and a reduced risk of gout.
Cherries and Cherry Juice:
Cherries and cherry juice have been linked to lower uric acid levels and a reduced risk of gout attacks due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
Some people believe that apple cider vinegar may help reduce uric acid levels.
You can try mixing a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar with a glass of water and consuming it daily. However, scientific evidence supporting this remedy is limited.
Herbal Remedies:
Certain herbs like nettle leaf, devil’s claw, and turmeric are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties and may be considered as supplements or herbal teas.
Consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies.
Weight Management:
Maintain a healthy weight or lose excess weight if you are overweight. Weight loss can help reduce uric acid levels.
Alcohol Moderation:
Limit alcohol consumption, particularly beer, and liquor, as alcohol can increase uric acid production and impede its elimination.
Lifestyle Changes:
Engage in regular physical activity to help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall health.
Avoid crash diets or fasting, which can lead to rapid weight loss and increased uric acid levels.
Get adequate sleep to support overall health.
It’s essential to note that natural remedies may not work for everyone, and individual responses can vary.
Moreover, if you have gout or other medical conditions related to high uric acid levels, your healthcare provider may recommend medications to manage uric acid levels more effectively.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary or lifestyle changes, and follow their guidance for the most appropriate and safe approach to managing uric acid levels and related conditions.
The causes of uric acid and home treatments.
While herbal remedies may have the potential in helping to reduce uric acid levels, it’s crucial to approach them with caution and consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal treatments, especially if you have gout or other medical conditions.
Here are some herbal remedies that are commonly suggested to help lower uric acid levels:
Devil’s Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens):
Devil’s claw is an herb known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It is believed to help reduce uric acid levels and relieve gout symptoms.
You can find devil’s claw supplements in various forms, such as capsules or teas. Also, follow the recommended dosage on the product label.
Nettle Leaf (Urtica dioica):
Its leaf is thought to have diuretic properties, which may aid in the elimination of uric acid from the body.
It helps to reduce the causes of uric acid and is one of the best treatments.
Nettle-leaf tea is a common preparation. Steep 1-2 teaspoons of dried nettle leaves in hot water and drink it a few times a day. You can find nettle leaf supplements as well.
Turmeric (Curcuma longa):
Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation associated with gout.
You can incorporate turmeric into your diet by adding it to curries, and soups, or taking it as a supplement. Follow product instructions for dosage.
Ginger (Zingiber officinale):
Ginger has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may be beneficial in managing gout symptoms.
Also, you can make ginger tea by steeping fresh ginger slices in hot water. Ginger can also be added to various dishes and smoothies.
Cherry Extract or Cherry Juice:
Cherries are known for their potential to reduce gout flares and lower uric acid levels.
You can consume fresh cherries, cherry extract supplements, or unsweetened cherry juice. Some studies suggest that consuming about 8-10 cherries a day may be beneficial.
Bromelain (from Pineapple):
This is an enzyme found in pineapple that may have anti-inflammatory properties.
Bromelain supplements are available but consult with a healthcare provider for proper dosing and use.
Green Tea (Camellia sinensis):
Green tea contains antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation and potentially lower uric acid levels.
You can consume green tea as a beverage or take green tea extract supplements. Follow recommended dosage instructions.
Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus):
It is rich in antioxidants and may have anti-inflammatory properties.
Bilberry supplements or extracts are available, but use them under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It’s important to note that herbal remedies can interact with medications or other health conditions, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before
incorporating them into your treatment plan. Due to various causes and varying responses, herbal treatments may not be effective for everyone’s uric acid. A healthcare
professional can provide guidance on the most suitable herbal treatments and monitor your progress to ensure they are safe and effective for your specific situation.